Production runs of small, intricate metal components have traditionally been addressed by metal injection molding or investment casting. Some manufacturers, however, are finding that advances in 3D printing technology can make it a cheaper and faster alternative.
The question of which manufacturing method is best suited to metal part production can be complicated. It’s not a decision that can be reached by weighing only a single factor. To arrive at the best decision, it’s important for businesses to consider many factors and prioritize.
Are fast lead times essential? Do the components have tensile, strength, or hardness requirements? Is surface finish a major consideration? While it’s important for businesses to weigh various priorities, the final cost-per-part (within quality specifications) is often the deciding factor in which technique wins out.
We’ve previously compared the costs of CNC machining and metal injection molding against those of metal additive manufacturing. Another option for manufacturers of complex parts, of course, is investment casting. This ancient technique has evolved to keep pace with industry and today remains a leading option for metal manufacturers. In this piece, we’ll look at how the cost of investment casting might break down in relation to metal AM in various scenarios.
Comparing Metal Additive Manufacturing & Investment Casting
Much of the literature available on this topic focuses on the synergies made possible by a hybrid technique using 3D printing to create patterns for molds. This works in some scenarios, but it’s usually much easier to choose one technique or the other.
To guide the cost analysis, it’s helpful to define the specifics of these situations. The final cost-per-part for both techniques will ultimately be determined by three main factors:
- Complexity of the part
- Part size
- Number of units
Investment Casting Process
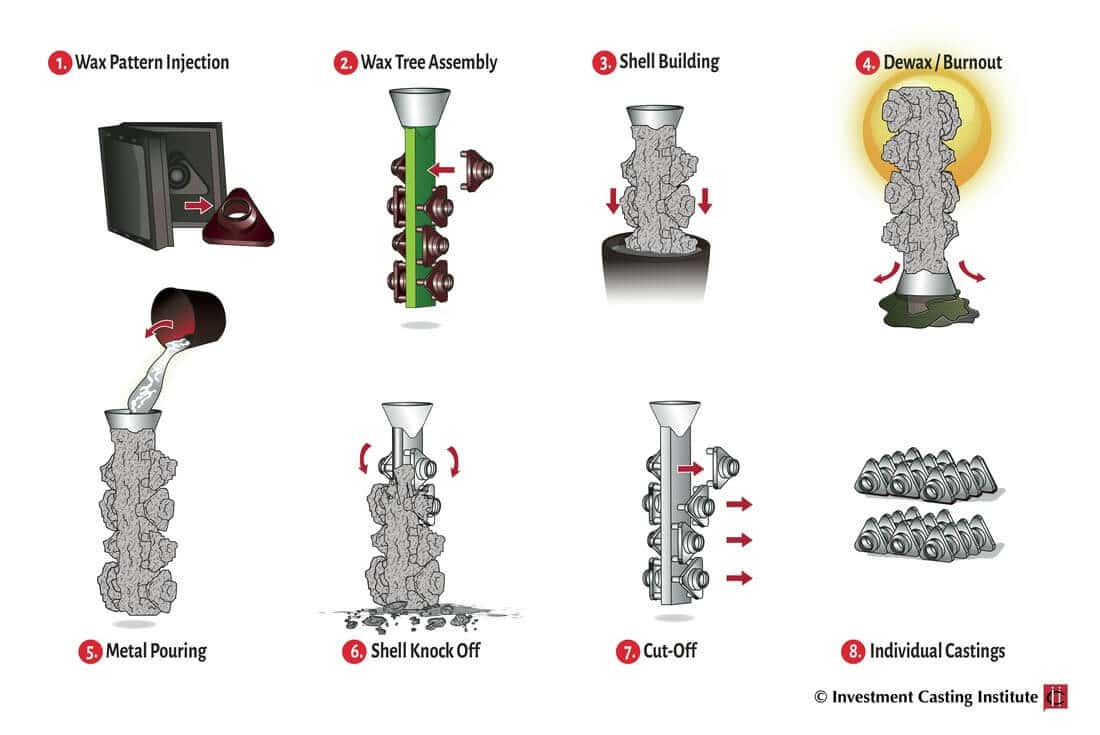
The investment casting process requires tooling to be made, and is a very manually intensive process. See the chart above for the eight basic steps to the casting process. Additional steps are added to ensure part quality requirements. Overall, the process is very manually intensive, which can lead to inconsistent part quality. Also, the tooling requires an up-front investment and limits design freedom after it is created.
Metal Additive Manufacturing
In comparison, metal 3D printing typically requires very little up-front investment. Printing requires optimization of the parameters, but the cost is negligible when compared to tooling. This also means that the time required to get to a first part is significantly less with AM.
Also, because the digital models direct the printer, it’s possible to update the CAD models and change the designs instantly, and at any time in new product development or in production. Complete design freedom is possible with metal 3D printing.
Study Compares Metal 3D Printing & Investment Casting
One fascinating study set out to cover the majority of the addressable market by creating cost comparisons for 75 specific situations. 3 different part sizes (4, 8, and 16 inches), 5 different production volumes, and 5 different parts of ascending complexity were used to compare 3D metal printing and investment casting side-by-side in real world terms. Quotes were obtained from actual manufacturers in both spaces to analyze costs as the inputs changed.
Final cost-per-part is influenced by complexity, production volume, and size.
The study found at industry-average price points, metal AM won out mostly in low-volume production of very small and detailed parts. Hybrid processes using printed patterns occupied the middle-ground of each, and investment casting excelled in situations involving lots of large, simple designs.
Interestingly, however, the study also considered the fact that innovation and economies of scale are rapidly driving costs down across the 3D printing industry as a whole. To that end, it examined the outcomes when the costs of metal 3D printing declined by fixed percentages. Suddenly, metal AM came out ahead in all but the largest runs of the largest parts. Here’s the kicker for manufacturers weighing this decision.
Rapidly Advancing Metal AM Technologies Driving Price Down
There are many new metal AM technologies on the cusp of breaking through to production. 3DEO’s Intelligent Layering® process is among the most efficient solutions on the market today for small-to-medium sized runs of complex metal parts. The resulting cost-per-part can be as much as 90% lower than other metal AM methods, and already directly competitive with investment casting for certain small, complex components.
Each situation is different, and metal AM will never be the one solution to all manufacturing problems. But it will certainly have its place in production manufacturing. Recent improvements have advanced the technology into a viable option for a wide range of scenarios.
3DEO’s Intelligent Layering®: Breaking the Mold of Price Per Part
Welcome to the brave new world of large-scale additive manufacturing.
3DEO’s revolutionary Intelligent Layering® can reduce the price per part by as much as 90% compared to other production options – and reducing costs is something everyone can agree on. 3DEO is committed to staying at the forefront of production in metal AM. Contact us here to discuss your part needs—metal 3D printing just might be the lowest cost option.
Contact 3DEO today to learn how our process can cut your parts cost.



